Blood Pressure: Understanding Causes, Risks, and Medication Management
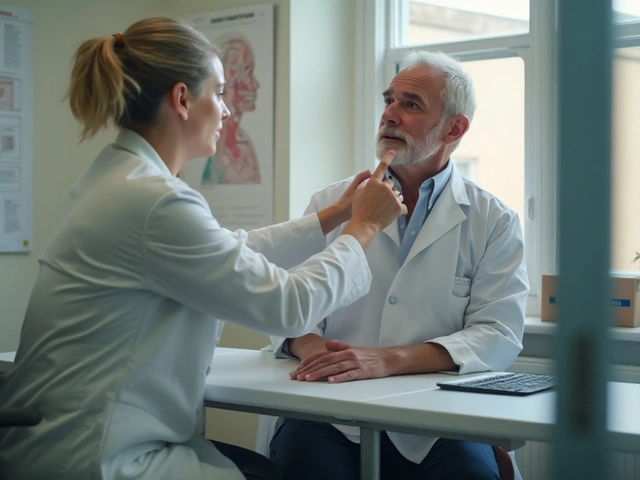
When your blood pressure, the force of blood pushing against artery walls. Also known as hypertension, it's one of the most common but silent threats to heart health in the U.S. Nearly half of American adults have it, and most don’t know until something serious happens—like a stroke or heart attack. High blood pressure doesn’t cause symptoms, but it slowly damages your arteries, heart, kidneys, and brain. It’s not just a number on a machine; it’s a warning sign your body is under constant strain.
Managing blood pressure, the force of blood pushing against artery walls. Also known as hypertension, it's one of the most common but silent threats to heart health in the U.S. often means taking medications like beta blockers, drugs that slow heart rate and reduce pressure by blocking adrenaline. Common examples include propranolol and metoprolol, used for decades to protect the heart. These aren’t just pills—they’re tools that prevent long-term damage. Some people also take anticoagulants, blood thinners that reduce clot risk, especially in those with atrial fibrillation. These are critical for stroke prevention, even if they raise fall risk in older adults. The key isn’t just lowering the number—it’s reducing the chance your arteries burst or your heart gives out. Many posts here dive into how these drugs work long-term, what side effects to watch for, and when switching to a generic version might change how you feel.
It’s not just about pills. High blood pressure ties into almost every other health issue: diabetes, kidney problems, sleep apnea, even anxiety. That’s why you’ll find posts about how statins affect your liver while lowering cholesterol, how antipsychotics can mess with your heart rhythm, and why stopping blood thinners after a fall can be more dangerous than the fall itself. This isn’t a one-size-fits-all condition. Your treatment needs to match your life—your age, your other meds, your activity level, your risks.
Below, you’ll find real, practical guides on what works, what doesn’t, and what to ask your doctor. Whether you’re on propranolol and wondering about weight gain, or you’re worried about how your generic blood pressure pill is doing, these posts give you the facts—not the fluff. No hype. No jargon. Just what you need to stay safe and in control.
Antihistamines and Blood Pressure: What You Need to Know
Antihistamines can affect blood pressure depending on the type. Second-gen options like loratadine and cetirizine are safe for most people with high blood pressure. Avoid decongestant combos. Monitor for dizziness or spikes.




![Buy Cheap Generic Cialis (Tadalafil) Online UK: Safe Options, Prices & Risks [2025]](/uploads/2025/08/thumbnail-buy-cheap-generic-cialis-tadalafil-online-uk-safe-options-prices-risks.webp)


