Antipsychotics: What They Are, How They Work, and Which Ones Actually Help
When someone is struggling with psychosis—hearing voices, holding false beliefs, or feeling disconnected from reality—antipsychotics, a class of medications designed to reduce or eliminate psychotic symptoms by balancing brain chemicals like dopamine. Also known as neuroleptics, these drugs are often the first line of treatment for conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe depression with psychotic features. They don’t cure these illnesses, but they can bring enough stability for people to live, work, and reconnect with their lives.
Not all antipsychotics are the same. Some, like Clozapine, a powerful medication used when other treatments fail, especially in treatment-resistant schizophrenia, work differently and carry unique risks. Clozapine requires regular blood tests because it can lower white blood cell counts, but for many, it’s the only thing that brings relief. Other common antipsychotics—like risperidone, olanzapine, and quetiapine—have fewer monitoring requirements but often come with weight gain, drowsiness, or movement problems. The choice isn’t just about effectiveness; it’s about matching the drug to the person’s body, lifestyle, and tolerance for side effects.
What you won’t find in most doctor’s office brochures is how messy this all gets in real life. One person might handle olanzapine fine and lose 30 pounds. Another might end up trembling or unable to sit still after just a few weeks on risperidone. And then there’s the stigma—many people stop taking these meds because they feel like they’re being turned into a zombie, even if the voices have quieted down. That’s why comparing options matters. You need to know what you’re signing up for before you start. That’s why the posts below dig into real comparisons: how antipsychotics stack up against each other, what monitoring is truly needed, and which ones are worth the trade-offs. You’ll see how Clozapine stands out, why some drugs are avoided unless absolutely necessary, and what to watch for when side effects creep in. This isn’t theory. It’s what people actually deal with—and what works when nothing else does.
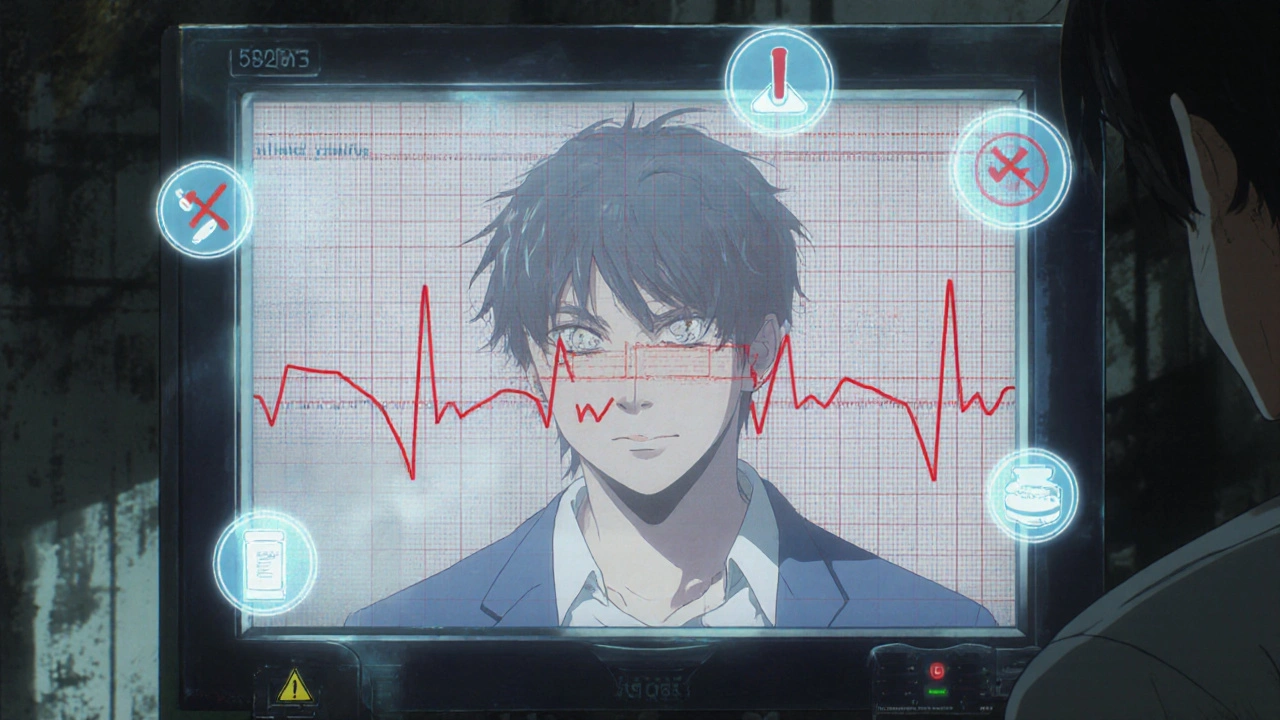
Antipsychotics and QT-Prolonging Drugs: What You Need to Know About Arrhythmia Risk
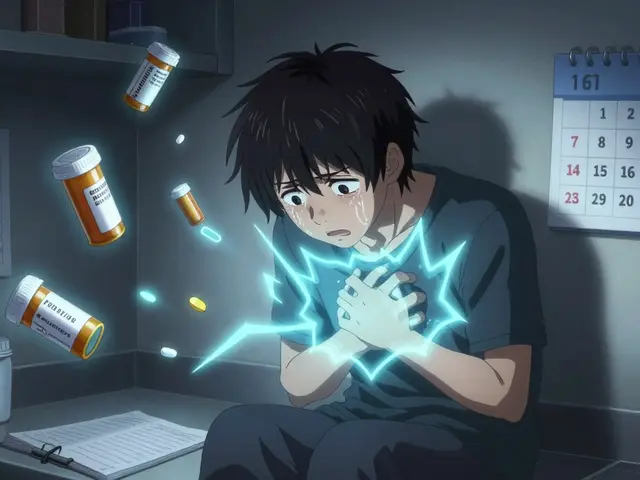
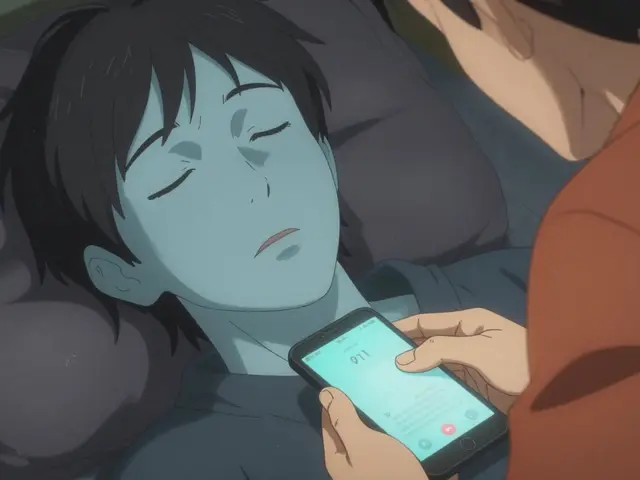
Combining antipsychotics with other QT-prolonging drugs can dangerously stretch the heart's electrical cycle, raising the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Learn which medications increase this risk, who's most vulnerable, and how to prevent life-threatening arrhythmias.